
- #Cve 2019 14287 exploit Patch#
- #Cve 2019 14287 exploit upgrade#
- #Cve 2019 14287 exploit full#
- #Cve 2019 14287 exploit password#
Luckily, that flaw could only be utilized in non-standard configurations, which implies that most systems with unsafe Sudo versions were left untouched. Not only this, but in 2019, another Sudo vulnerability was traced as CVE-2019-14287, and it enabled unauthorized users to run commands as root. Vulnerable systems will deliver an error beginning with “sudoedit:” on the other side, the patched ones will demonstrate an error starting with “usage:” However, the experts have affirmed that if any user wants to test if their system is vulnerable, they can do so as a non-root user and run the “sudoedit -s /” command. (pwfeedback is a default setting in Linux Mint and elementary OS however, it is NOT the default for upstream and many other packages, and would exist only if enabled by an administrator. The vulnerability was initially introduced in the Sudo program nearly 9 years ago, in July 2011, with commit 8255ed69, and it hits the default configurations of all steady versions from 1.9.0 to 1.9.5p1 and all the legacy versions from 1.8.2 to 1.8.31p2. In Sudo before 1.8.26, if pwfeedback is enabled in /etc/sudoers, users can trigger a stack-based buffer overflow in the privileged sudo process. The sudo vulnerability CVE-2019-14287 is a security policy bypass issue that provides a user or a program the ability to execute commands as root on a Linux system when the 'sudoers configuration' explicitly disallows the root access. Before the disclosure, Baron Samedit fixed
In a Linux system a user can execute programs as other users by specifying their UID using the command sudo -uidMoreover, there are other operating systems and distributions that are recommended by Sudo that are apparently also exploitable using CVE-2021-3156 exploits. The CVE-2019-14287 vulnerability gives to a local user or a program the ability to execute commands as a superuser.
#Cve 2019 14287 exploit full#
And using all these exploits the security researchers were able to get full root privileges on various Linux distributions.Īll these distributions include Debian 10 (Sudo 1.8.27), Ubuntu 20.04 (Sudo 1.8.31), and Fedora 33 (Sudo 1.9.2). That’s why Qualys has produced three CVE-2021-3156 exploits to showcase how potential threat actors can successfully exploit this vulnerability.
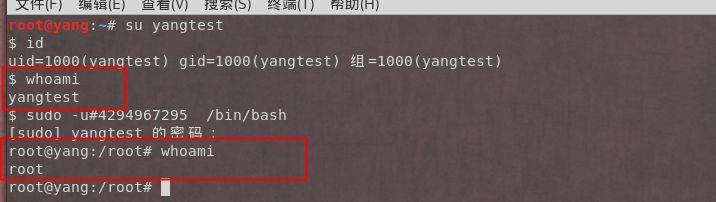
#Cve 2019 14287 exploit password#
However, Sudo before 1.9.5p2 has the heap-based buffer overflow, and it can be exploited by any local user, and here the attackers not being compelled to know the user’s password to exploit the flaw successfully. This vulnerability was revealed by the security researchers from Qualys, who revealed it on January 13th and made sure that all the patches are possible before going public with their conclusions. CVE-2019-14287 vulnerability allows malicious users to exploit locally certain sudoers configurations that allow to run commands as other unprivileged users. Sudo before 1.9.5p2 has a Heap-based Buffer Overflow, enabling all kinds of privilege escalation to root via “sudoedit with -s or -i flags” and provide a command-line argument that concludes with a single backslash character.
#Cve 2019 14287 exploit Patch#
System administrators should check with their product vendors to confirm if their Linux systems are affected and the availability of the patch, and if so, apply the patch or follow the recommendations provided by the product vendors to mitigate the risk.It acts on the principle of most limited privilege, where the program provides enough permission to the people so that they can get their jobs done without negotiating the overall protection of the system. 1 Attacker Value Low (5 users assessed) Exploitability Very High (5 users assessed) User Interaction None Privileges Required Low Attack Vector Network 1 CVE-2019-14287 Disclosure Date: Octo (Last updated June 05, 2020) CVE-2019-14287 CVSS v3 Base Score: 8. Successful exploitation could lead to elevation of privilege on an affected system.Ī patch for the vulnerability is available for some of the Linux distributions, such as Debian and Ubuntu. The open source tool lets system administrators set security policies that allow certain users to execute commands as the superuser (root user) or another user.
#Cve 2019 14287 exploit upgrade#
Users should upgrade to the latest version or arrange migrating to other supported technology.

Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 will not receive the relevant patch. Please note that Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 has reached the end of maintenance provided by Red Hat on 31 March 2017.

This vulnerability could only be exploited if the configuration file of Sudo is written to allow a user to run a command as any user except root. A local attacker can exploit this vulnerability by providing an invalid user ID while requesting to run a command as root. A privilege escalation vulnerability was identified in Sudo package.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
